Overview
Localization of PET image using structural MRI image requires a rigid-body intra-subject co-registration of PET and T1 images. We examined multiple registration techniques and our visual and quantitative evaluation showed that ART is the most suitable tools for addressing this co-registration problem.
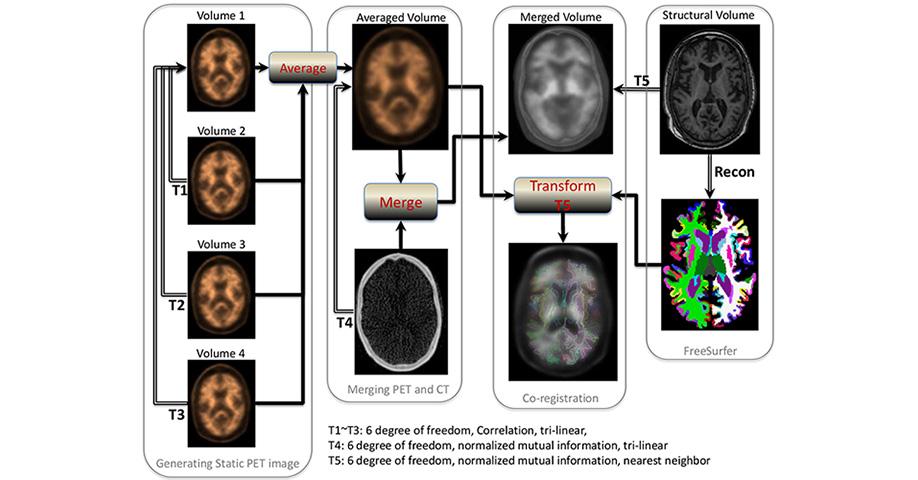
The outline of the process of this localization start by aligning Dynamic PET frames (4 scans) to the first frame using rigid-body registration and a static PET image was obtained by averaging the four registered frames. The static PET image was then registered with the CT to obtain the transformation matrix that its inverse transfers CT image to static PET image space. The CT and static PET image were merged to generate a composite image in the PET static space.
Each individual’s structural T1 image in FreeSurfer space was also registered to the participant’s merged image using normalized mutual information and tri-linear interpolation to obtain the second transformation matrix. A combination of the two transformation matrices was used to transfer the 4 regional masks and the cerebellar gray matter from FreeSurfer space to static PET image space using nearest neighbor interpolation. These 4 regional masks in static PET space were used to extract the regional PET data. The procedures are summarized in Figure 1.
The standardized uptake value (SUV), defined as the decay-corrected brain radioactivity concentration normalized for injected dose and body weight, was calculated at selected regions. The SUV was then normalized to cerebellum to derive the standardized uptake value ratio (SUVR), which was the measurement used in the analyses. Analyses incorporated both the individual ROIs (including TMP, PAR, CG, and FRC) and an overall mean value of amyloid burden across the ROIs.
Related Publication
A.M. Brickman, V.A. Guzman, M. Gonzalez, Q. R. Razlighi, Y. Gu, A. Narkhede, S. Janicki, M. Ichise, Y. Stern, J.J. Manly, N. Schupf, R.S. Marshall, “Cerebral autoregulation, beta amyloid, and white matter hyperintensities are interrelated,” Neuroscience Letters, vol. 592, pp 54–58, 2015.
Y. Gu, Q. R. Razlighi, L. B. Zahodne, S. C. Janicki, M. Ichise, J. J. Manly, D. P. Devan and, A. M. Brickman, N. Schupf, R. Mayeux, Y. Stern, “Brain amyloid deposition and longitudinal cognitive decline in nondemented older subjects: results from a multi-ethnic population,” PLoS One, 2015.
H. Oh, J. Steffener, Q. R. Razlighi, C. Habeck, D. Liu, Y. Gazes, S. Janicki, Y. Stern, “Aβ-related hyperactivation in frontoparietal control regions in cognitively normal elderly,” Neurobiology of Aging, vol. 36, no. 12, pp 3247-3254, Dec. 2015.
H. Oh, J. Steffener, Q. R. Razlighi, C. Habeck, and Y. Stern , “Beta-amyloid deposition is associated with decreased right prefrontal activation during task switching among cognitively normal elderly”, Journal of Neuroscience, In Press, Jan. 2016.
Software Released
Please contact Dr. Razlighi for the code and instruction.

